Recently, the research result Ligand recognition and allosteric regulation of DRD1-Gs signaling complexes participated by the G Protein Coupled Receptor and Drug Development Team of School of Pharmacy was published online in the journal Cell.
This study used single-particle cryo-electron microscopy technology to analyze for the first time catechol agonists (pleasure hormone Dopamine, clinical drug Fenoldopam for lowering blood pressure, full agonist A77636, G protein preference agonist SKF83959), non-catechol agonists PW0464 and the positive allosteric modulator LY3154207 activating the three-dimensional structure of the dopamine receptor DRD1 and the downstream Gs trimer to form a complex. This study analyzed the structure of the dopamine receptor DRD1-Gs complex for the first time, and explained in detail the mechanism of DRD1 ligand recognition, allosteric regulation, and coupling with G protein at the atomic level, which brings new hope for drug development and treatment of kidney injury and other diseases.
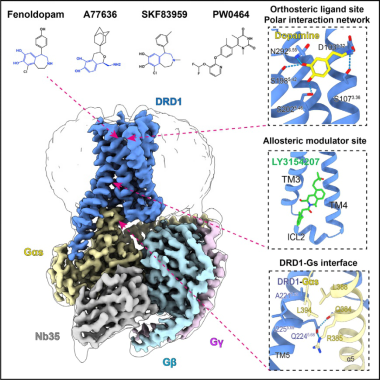
Figure 1 Ligand recognition and allosteric regulation of DRD1-Gs signaling complex
The G protein coupled receptors and drug development research team was established in 2019 in the School of Pharmacy of Binzhou Medical University (BMU). The leader, Professor Jinpeng Sun, is a distinguished professor in BMU. Since its establishment, members of the team have received 3 National Natural Science Foundation grants (including 1 general project and 2 youth fund projects) with 2 SCI papers published in Journal of Pharmacology and Journal of Biological Chemistry, with Binzhou Medical University as the first author unit. Professor Sun Jinpeng is the co-corresponding author of the Cell paper, and the team member Dr. Daolai Zhang and our graduate student He Yonghao are the participating authors of the paper. It is the first time that teachers and students of our University have participated in the publication of academic papers in Cell. It is of great significance to further enhance the ESI global ranking of our University, promote the construction of disciplines, and enhance the popularity of BMU.

Article link:
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(21)00071-4
BY: Zhang Daolai
SOURCE: School of Pharmacy (Wine School)





