On November 7, LILRB4 ITIMs mediate the T cell suppression and infiltration of acute myeloid leukemia cells by Associate Professor Li Zunling from the immunology research team of the university was published online in the journal Cellular and Molecular Immunology.
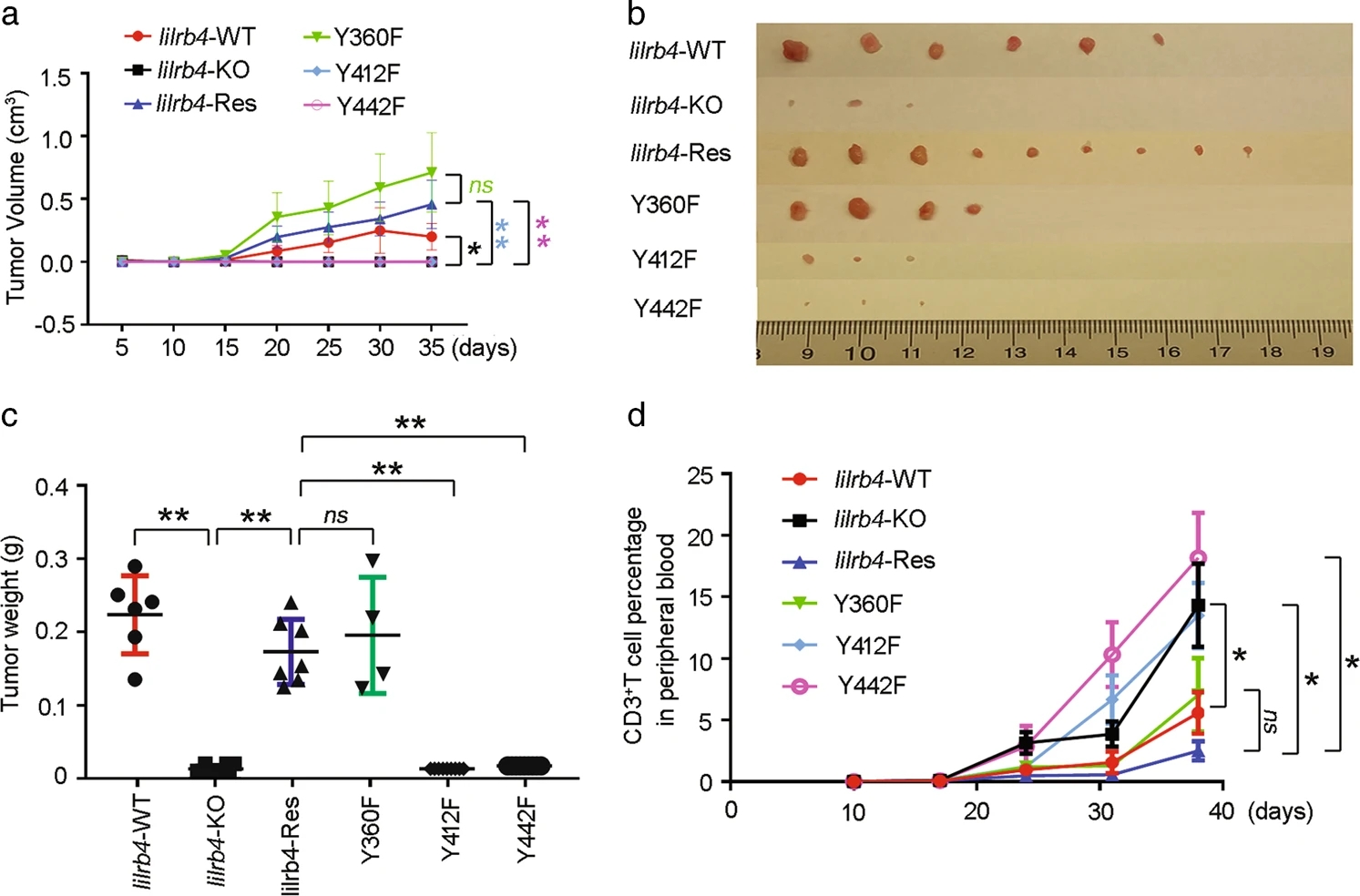
Based on the previous article in Nature, this study further explored the molecular mechanism of immunosuppressive receptor LILRB4 mediated T cell proliferation suppression and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) extramedullary infiltration. The study mainly solved two problems. First, it clarified the role of the three ITIM (immunoreceptor tyrosine inhibitory motifs) motifs in LILRB4 cells in the process of T cell proliferation inhibition and AML cell extramedullary infiltration. The results of the study show that: ITIM1 (VTY360AKV) and ITIM2 (VTY412ARL) mediate the inhibition of T cell proliferation, but ITIM1, ITIM2 and ITIM3 (SVY442ATL) are all involved in the extramedullary infiltration of AML cells. Second, LILRB4 and LILRB1 are exchanged in extracellularly structural domains and intracellular ITIMs motifs to construct chimeric expression vectors. In vivo and in vitro experimental results show that although the LILRB family members have similar ITIMs sequences, LILRB1 cannot mediate T cell proliferation inhibition and extramedullary AML cells Infiltration, suggesting that LILRB4 has a unique function in AML cells. This study provides a good target for the development of AML cell therapy drugs.
Cellular and Molecular Immunology is a JCR medical journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in immunology II. The latest impact factor is 8.213. This is another high-level paper with complete intellectual property rights of the university. Associate Professor Li Zunling is the first author, and Binzhou Medical University is the first completion unit.
Article link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-019-0321-2
BY: Liang Shaohua
SOURCE: School of Basic Medical Sciences





