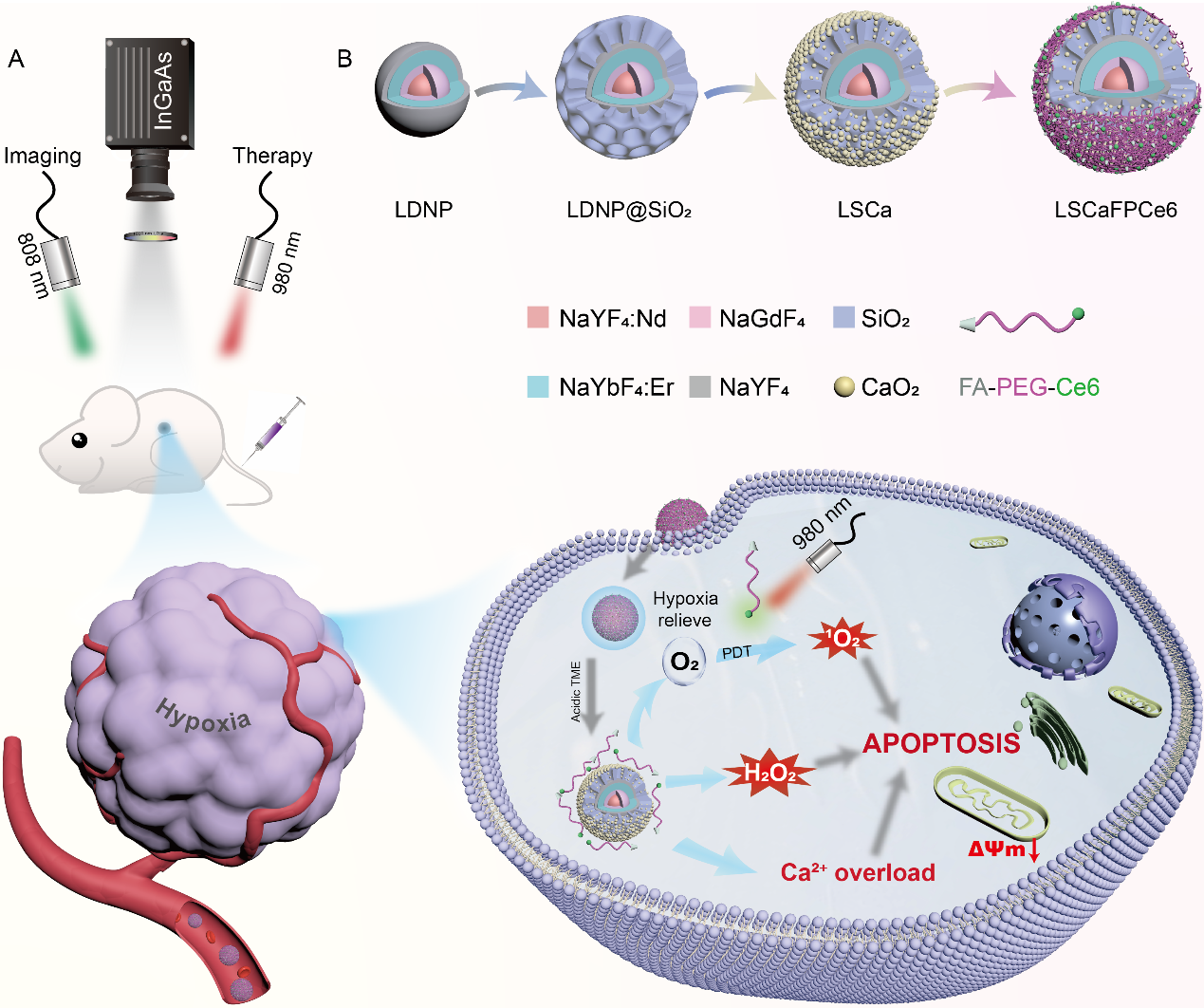
Recently, the latest research result of the precision medicine research team was accepted by Small, a top professional journal in the field of biomaterials (SCI Regional I, TOP journal of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Impact Factor 15.153). The research result is titled NIR-II Fluorescence Imaging-guided Oxygen Self-sufficient Nano-platform for Precise Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy, which is the first to propose a photodynamic therapy (PDT) strategy for enhancing hypoxic tumors under the guidance of NIR-II fluorescence.
The research pointed out that solid tumors often grow out of control and tumor vascular development is relatively lagging behind, resulting in a hypoxic state of solid tumors. Traditional photosensitizers need to consume oxygen during photodynamic therapy, leading to further deterioration of the hypoxic environment, which results in the failure to achieve therapeutic effect in hypoxic areas and great limitation of the effect of photodynamic therapy. It is of great significance for precise tumor treatment and systemic toxicity reduction to solve the problem of tumor hypoxia and achieve sustained and efficient specific photodynamic therapy. In order to solve the problem, the precision medicine research team designed and prepared a NIR-II imaging-guided LSCaFPCe6 nanomedicine. The medicine has good O2, hydrogen peroxide and Ca2+ supply characteristic, which can effectively alleviate intracellular hypoxia, thereby enhancing ROS and Ca2+ overload-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, NIR-II fluorescence imaging guidance enables non-invasive monitoring of nanomedicine accumulation in tumors in situ, thus accurately indicating the optimal triggering time of PDT. The above work effectively addresses the problem of hypoxia during tumor PDT with excellent biosafety and anti-tumor effects.
Li Wenling, a master's student in the School of Pharmacy, Class of 2020, is the first author of the paper with Professor Tian Geng, Professor Zhang Guilong and Professor Liu Lu as co-corresponding authors. This paper is a new high-level research breakthrough of the precision medicine research team following the papers published in the Chemical Engineering Journal, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Journal of Nanobiotechnology and other Region I journals of the Chinese Academy of Sciences since this year. The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Shandong Provincial Higher Education Institution’ s Innovative Young Talents Introduction and Cultivation Program, Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and Research Start-up Funds of Binzhou Medical University.

Link to the paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202205647
SOURCE: School of Pharmacy (Wine School)
BY: Jiang Wenguo





